Abstract
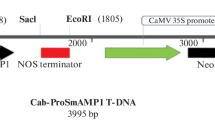
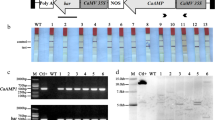
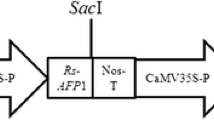
Plasmids, pCA1 and pCWEA1, carrying antimicrobial peptide gene(s), Ac-AMP1.2 and ESF12, were used to transform hybrid poplar clones Ogy and NM6. Peptide Ac-AMP1.2 is an analog of Ac-AMP1 which is one of the smallest chitin-binding proteins. Synthetic peptide ESF12 mimics the amphipathic α-helix found in magainins. Transgene mRNA was detected in the transformed plants. When evaluated for resistance to hybrid poplar pathogen Septoria musiva with an in vitro leaf disk assay, the transformed Ogy plants showed significantly increased pathogen resistance as compared to the untransformed Ogy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1995) Short Protocols in Molecular Biology. Toronto: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Broekaert WF, Marien W, Terras FRG, Bolle MFC, de Proost P, van Damme J, Dillen L, Claeys M, Rees SB, Vanderleyden J (1992) Antimicrobial peptides from Amaranthus caudatus seeds with sequence homology to the cysteine/glycine-rich domain of chitin-binding proteins. Biochemistry 31: 4308-4314.
Campbell WH, Gowri G (1990) Codon usage in higher plants, green algae, and cyanobacteria. Plant Physiol. 92: 1-11.
Cary JW, Rajasekaran K, Jaynes JM, Cleveland TE (2000) Transgenic expression of a gene encoding a synthetic antimicrobial peptides results in inhibition of fungal growth in vitro and in planta. Plant Sci. 154: 171-181.
Florack D, Allefs S, Bollen R, Bosch D, Visser B, Stiekema W (1995) Expression of giant silkmoth cecropin B genes in tobacco. Transgenic Res. 4: 132-141.
Hancock RE, Lehrer R (1998) Cationic peptides: a new source of antibiotics. Trends Biotechnol. 16: 82-88.
Heuchelin SA, McNabb Jr HS, Klopfenstein NB (1997) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Populus × euramericana Ogy using the chimeric CaMV 35S-pin2 gene fusion. Can. J. For. Res. 27: 1041-1043.
Hobbs SLA, Warkentin TD, DeLong CMO (1993) Transgene copy number can be positively or negatively associated with transgene expression. Plant Mol. Biol. 21: 17-26.
Hollick JB, Gordon MP (1993) A poplar tree proteinase inhibitorlike gene promoter is responsive to wounding in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol. 22: 561-572.
Huang Y, Nordeen RO, Di M, Owens LD, McBeath JH (1997) Expression of an engineered cecropin gene cassette in transgenic tobacco plants confers disease resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv tabaci. Phytopathology 87: 494-499.
Ko K, Norelli JL, Reynoird JP, Boresjza-Wysocka E, Brown SK, Aldwinckle HS (2000) Effect of untranslated leader sequence of AMV RNA 4 and signal peptide of pathogenesis-related protein 1b on attacin gene expression, and resistance to fire blight in transgenic apple. Biotechnol. Lett. 22: 373-381.
Li Q, Lawrence CB, Xing HY, Babbitt RA, Bass WT, Maiti IB, Everett NP (2001) Enhanced disease resistance conferred by expression of an antimicrobial magainin in transgenic tobacco. Planta 212: 635-639.
Liang H, Maynard CA, Allen RD, Powell WA (2001) Increased Septoria musiva resistance in transgenic hybrid poplar leaves expressing a wheat oxalate oxidase gene. Plant Mol. Biol. 45: 619-629.
Lo MH, Abrahamson LP, White EH, Manion PD (1995) Early measures of basal area and canker disease predict growth potential of some hybrid poplar clones. Can. J. For. Res. 25: 1113-1118.
McNabb Jr HJ, Ostry ME, Sonnelitter RS, Gerstenberger PE (1982) The effect and possible integrated management of Septoria musiva in intensive, short-rotation culture of Populus in the north central states. In: Zavitkovski WIJ, Manhattan EH, eds. Proceedings of the North American Poplar Council Meeting, July 20-22, Rhinelander. Wisconsin: Division of Extension, Kansas State University, pp. 51-58.
Moore LM, Wilson LP (1983) Recent advances in research of some pest problems of hybrid Populus in Michigan and Wisconsin. Gen. Tech. Rep. North Centr. For. Exp. Station 91: 94-101.
Ostry ME, McNabb Jr HS (1983) Diseases of intensively cultured hybrid poplars: a summary of recent research in the north central region. Gen. Tech. Rep. North Centr. For. Exp. Station 91: 102-109.
Ostry ME, McNabb Jr HS (1985) Susceptibility of Populus species and hybrids to disease in the North Central United States. Plant Dis. 69: 755-75.
Ostry ME, McRoberts RE, Ward KT, Resendez R (1988) Screening hybrid poplars in vitro for resistance to leaf spot caused by Septoria musiva. Plant Dis. 72: 497-499.
Powell WA, Maynard CA (1997) Designing small antimicrobial peptides and their encoding genes. In: Klopfenstein N, Chun YW, Kim M-S, Ahuja MR, eds. Micropropagation, Genetic Engineering and Molecular Biology of Populus, Fort Collins, CO: Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station, pp. 165-172.
PowellWA, Catranis CM, Maynard CA (1995) Synthetic antimicrobial peptide design. Mol. Plant-Microb. Interact. 8: 792-794.
Powell WA, Catranis CM, Maynard CA (2000) Design of selfprocessing antimicrobial peptides for plant protection. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 31: 163-168.
Pröls F, Meyer P (1992) The methylation patterns of chromosomal integration regions influence gene activity of transferred DNA in Petunia hybrida. Plant J. 2: 465-475.
Putterill JJ, Gardner RC (1989) Initiation of translation of the betaglucuronidase reporter gene at internal AUG codons in plant cells. Plant Sci. 62: 199-205.
Raikhel NV, Lee H-L (1993) Structure and function of chitin0 binding proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 44: 591-615.
Staub JM, Maliga P (1995) Expression of a chimeric uidA gene indicates that polycistronic mRNAs are efficiently translated in tobacco plastids. Plant J. 7: 845-848.
Wan CY, Wilkins TA (1994) A modified hot borate method significantly enhances the yield of high-quality RNA from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Anal. Biochem. 223: 7-12.
Yang D, Bernier L, Dessureault M (1994) Biological control of Septoria leaf spot of poplar by Phaeotheca dimorphospora. Plant Dis. 78: 821-825.
Zasloff M (1987) Magainins, a class of antimicrobial peptides from Xenopus skin: isolation, characterization of two active forms, and partial cDNA sequence of a precursor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 5449-5453.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, H., Catranis, C.M., Maynard, C.A. et al. Enhanced resistance to the poplar fungal pathogen, Septoria musiva, in hybrid poplar clones transformed with genes encoding antimicrobial peptides. Biotechnology Letters 24, 383–389 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014552503140
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014552503140